Candy Mountain becomes Washington’s 16th American Viticultural Area
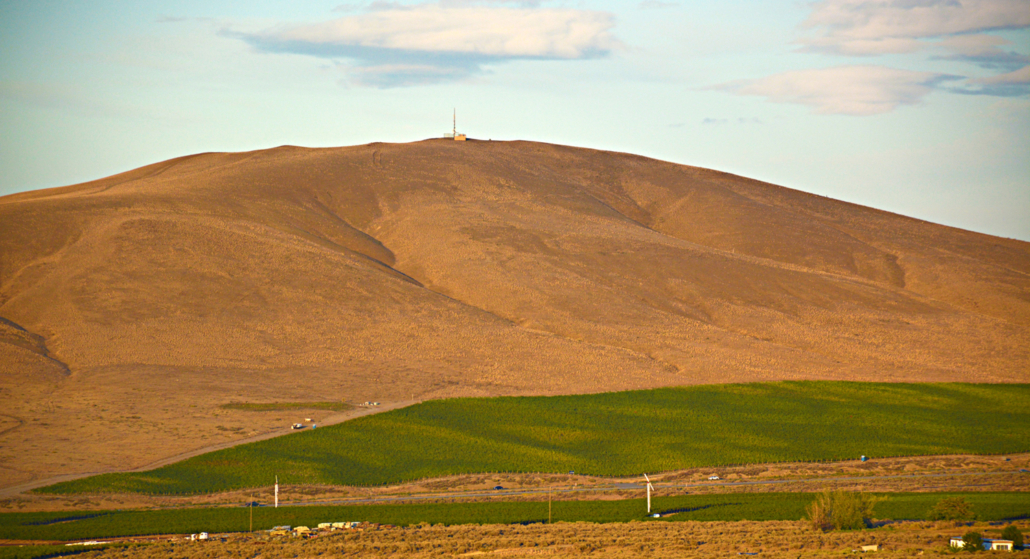

Candy Mountain, located just outside the Southwest Washington Cities of Richland and West Richland, became Washington State’s 16th official AVA on Sept. 25. Photo by Kevin Pogue.
On Sept. 25, 2020, Candy Mountain was officially designated by the U.S. Alcohol and Tobacco, Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) as Washington State’s 16th American Viticultural Area. At 815 acres, Candy Mountain is the smallest AVA in Washington. It sits to the southeast of Red Mountain and is within the Yakima Valley AVA and the larger Columbia Valley AVA.
As part of making Candy Mountain the state’s newest AVA, TTB also expanded the boundary of the existing Yakima Valley AVA by 72 acres to fully encompass the Candy Mountain AVA. As a point of reference, Candy Mountain is located to the northeast of the intersection of Interstate Highways I-82 and I-182 near the cities of Richland and West Richland, WA.
“Candy Mountain is small but mighty,” said Steve Warner, president of the Washington State Wine Commission. “The region has been growing highly regarded grapes for years, so it will be great to finally see the AVA-designated wines out in the world.”
Candy Mountain is part of a chain of four mountains in the area, which also include Red Mountain, Badger Mountain, and Little Badger Mountain. It has a number of similarities to Red Mountain, including a warm climate and higher winds relative to the surrounding area. According to Kevin Pogue PhD, who wrote the AVA petition for Candy Mountain, its distinct characteristics include:
- The AVA is located on an isolated mountain with excellent cold air drainage that rises above lower elevation plains.
- A very large percentage of the AVA faces to the south, enhancing solar radiation and allowing the soils to warm quickly in the spring.
- The soils, especially on the upper slopes, are shallower than those of the surrounding plains, allowing vine roots to penetrate to the underlying basalt bedrock or ice age flood deposits.
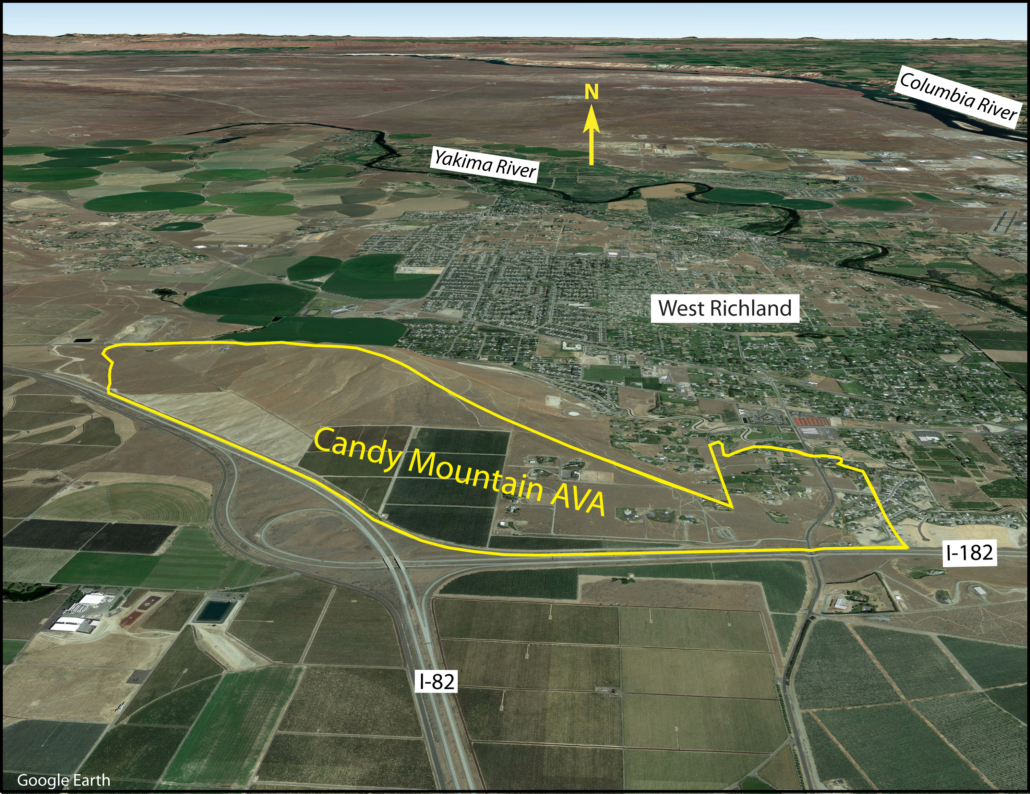
Google Earth captures the boundaries of Candy Mountain, Washington State’s newest, and smallest AVA at 815 acres. Photo courtesy Kevin Pogue.
The soils of Candy Mountain are composed of wind-deposited silt and sand that overlies silt, sand, and gravel deposited by ice age floods on the lower slopes of the mountain, and basalt bedrock on the upper slopes. There are currently 110 acres of vineyards planted in the AVA, and almost all are red varieties.
“The fruit from Candy Mountain is highly regarded,” Pogue said. “There’s new acreage going in right now and I think it has the potential to be one of the most visible AVAs in Washington. Winemakers who have used the fruit are very impressed with the quality.”
Vineyards currently growing grapes on Candy Mountain include Shaw Vineyards, Kitzke Estate’s Candy Mountain Vineyard and Candy Mountain Hill Vineyard, jointly owned by Dick Shaw and Ramer Holton.
Candy Mountain comes on the heels of Royal Slope becoming Washington’s 15th AVA on Sept 2. To qualify as an AVA, a wine grape-growing region must be distinguishable by features such as climate, soil, elevation and physical features. One month after being designated as an official AVA, wineries that use the grapes of the new AVA in producing their wines may submit a Certificate of Label Approval (COLA) request to TTB for a label using the AVA name as an appellation of origin.
“The process to establish a new AVA takes years, so we’re excited to see these two come to fruition,” Warner said. “There are several more AVAs currently under petition to be approved in the coming years, which is another positive sign of the continued growth of the Washington wine industry. With more than 1,000 wineries, 60,000 acres of vineyards and now 16 AVAs, we’re still only just getting started.”
About the Washington State Wine Commission:
The Washington State Wine Commission (WSWC) represents every licensed winery and wine grape grower in Washington State. Guided by an appointed board, WSWC provides a marketing platform to raise positive awareness about the Washington wine industry and generate greater demand for its wines. Funded almost entirely by the industry through assessments based on grape and wine sales, WSWC is a state government agency, established by the legislature in 1987. To learn more, visit www.washingtonwine.org.



